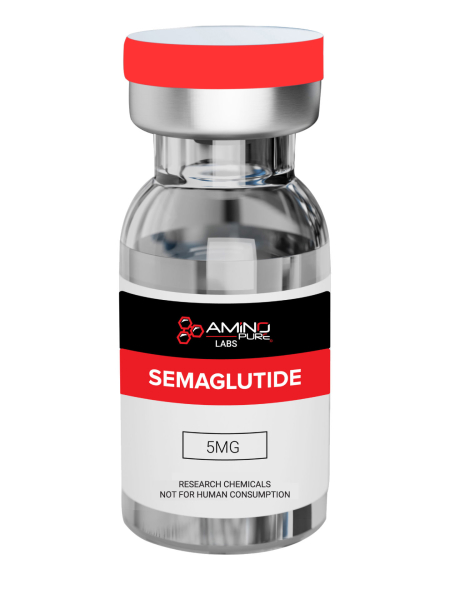
SEMAGLUTIDE 5MG
$139.99 – $849.99
Semaglutide, GLP-1, is a naturally occurring peptide known to lower blood sugar levels and enhance insulin secretion. Research shows that GLP-1 may also improve heart, liver, and lung function while helping to slow or prevent the effects of Alzheimer’s disease. GLP-1 has been shown to significantly decrease appetite by delaying gastric emptying and reducing intestinal motility. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Analog Shown to Stimulate Insulin and Suppress Glucagon Secretion in a Glucose-Dependent Manner
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
RESEARCH CHEMICALS ONLY
Description
NOT FOR HUMAN CONSUMPTION
Additional information
| size | QTY 1, QTY 2, QTY 3, QTY 5, QTY 10 |
|---|